Thermal analyses are an important part of modern design processes in various industrial sectors. By leveraging advanced CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) technologies, engineers can model thermal phenomena with high precision. This allows for better thermal energy management within systems, identification of areas which require modifications to enhance reliability and improve efficiency of the developed devices and structures.
Thermal simulations are not only an optimisation tool but, also a key process in terms of meeting strict standards and technical specifications. CAE technology makes it possible to precisely depict the equipment operating conditions and analyse potential problems that could affect its operation.
The most common applications of thermal simulations are:
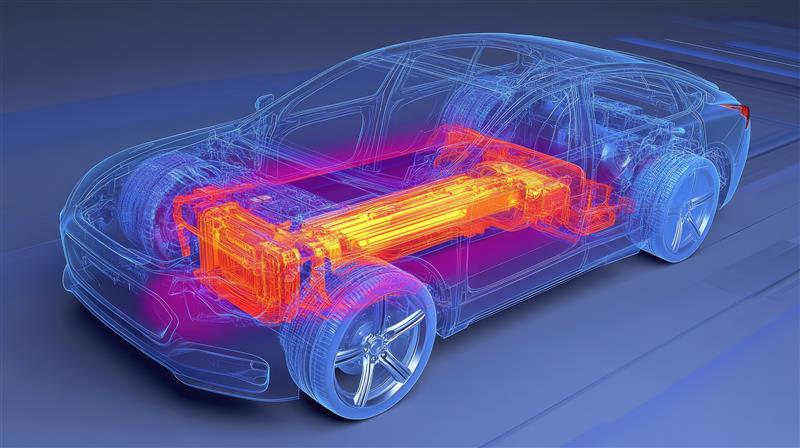
Thermal simulations support design processes in many industries, help to optimise designs and to reduce risks of failure. Here are examples of applications in individual sectors:
During the design of a car, thermal analysis is used in the creation of cooling systems for combustion, electric and hybrid propulsion. These simulations allow for the optimisation of heat management systems, which translates into greater vehicle efficiency, reduced fuel consumption and better performance. Application examples:
In the design of commercial vehicles and buses, flow and thermal simulations play an important role in the design of HVAC (heating, ventilation, air conditioning) systems. They enable system development for comfortable passenger traveling and minimum energy consumption. These simulations are also being used to analyse the thermal management of drive systems and electronic components.
Rail vehicles such as trains and trams require reliable cooling systems for their drive and electrical systems. In the design of rail vehicles, thermal simulations support the design of components that are resistant to changing operating conditions and to the high temperatures generated during braking. These analyses also help to improve passenger comfort by optimising ventilation systems. HVAC is also standard in Rail cars and locos today.
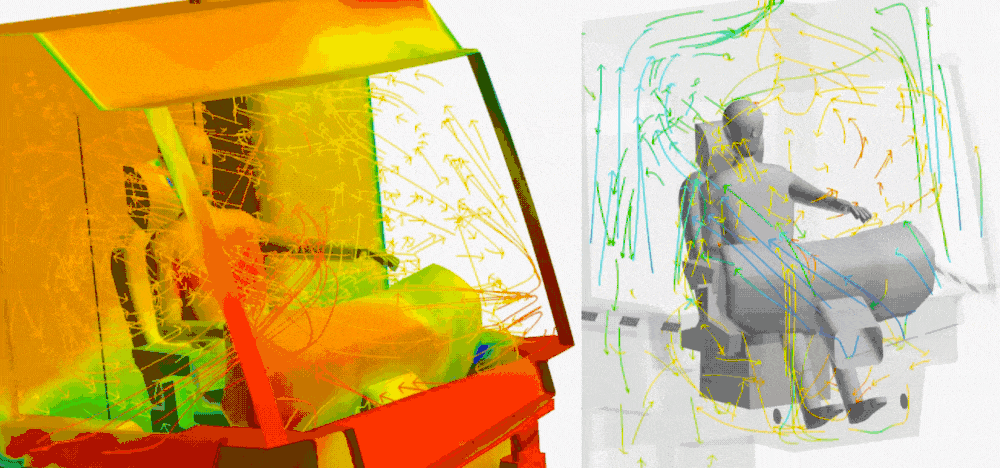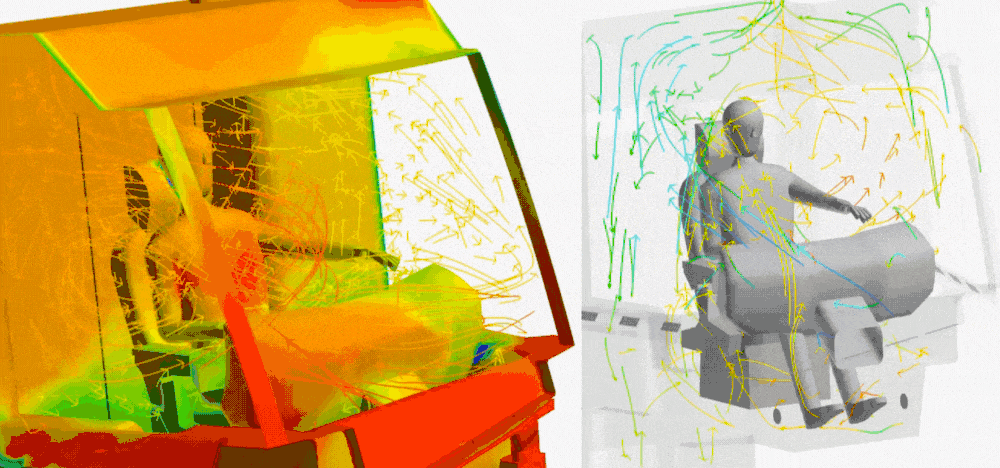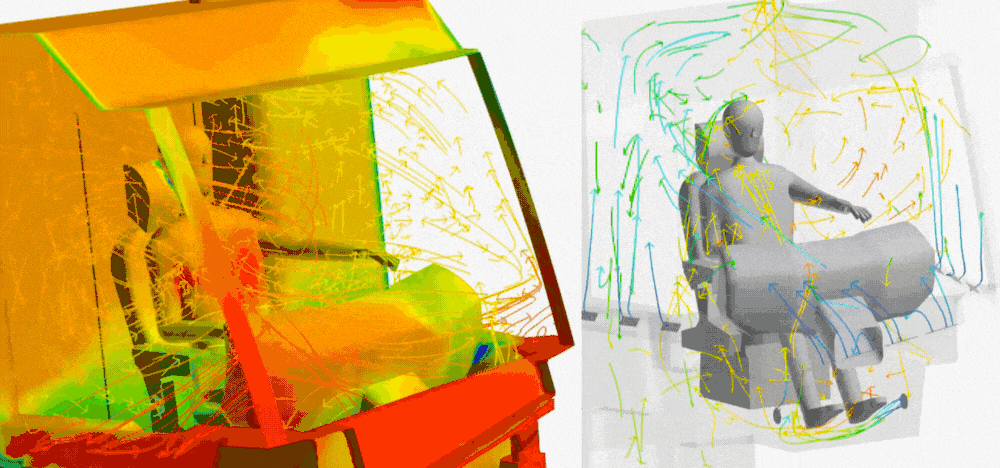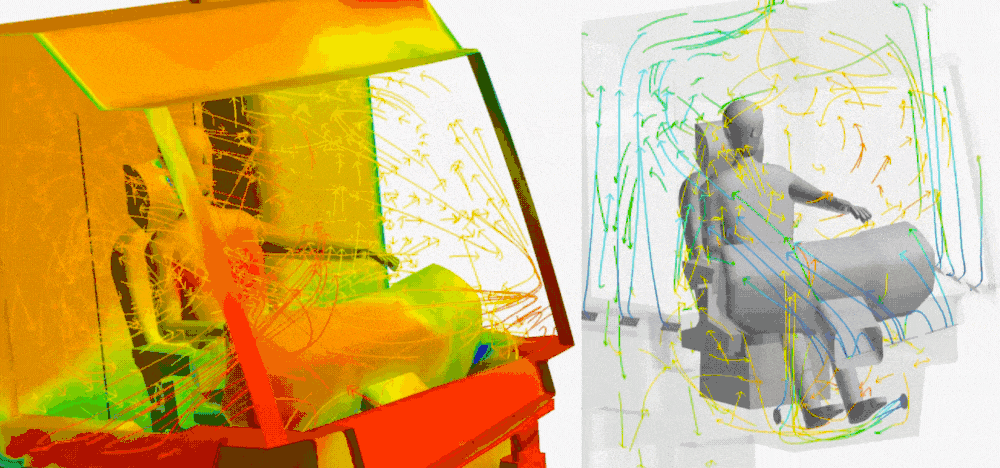
In the design of working machines and the design of agricultural machines, thermal simulations support the design of cooling systems that must operate reliably under difficult working conditions. Optimisation of cooling systems, engines and hydraulic systems is the key to extending the lifespan of machines and improving their efficiency. HVAC is today standard in the personnel cabins.
Thermal simulations which use CAE technology are an important tool in the design process of modern equipment. These analyses allow for the identification of potential problems, and system optimisation for increased efficiency and safety.
Endego offers comprehensive services in the field of computer-aided engineering simulations. Our team consists of experienced experts who successfully carry out even the most demanding projects and have application feedback, verification and experience.
Our offer includes, among others:
Endego carries out comprehensive thermal analyses, supporting various industries, such as automotive, public transport and railway by use of the most modern tools and the wide experience of its specialists. Choosing Endego to be your partner, you get access to advanced technologies and wide knowledge of the expert team who successfully carry out even the most complex tasks. Contact us to learn more about our services and opportunities for cooperation!
The past few years have been challenging for the European automotive sector – production declines, supply chain disruptions, and intensifying competition from Asian manufacturers have forced many companies to downsize. Now, as the market slowly begins to recover, businesses face a new challenge: how to quickly restore their delivery capacity when skilled specialists are in short supply?
Read moreModern automotive lighting is no longer limited to a purely functional role. LED logos, illuminated grilles, and dynamic light animations are becoming a new communication language for car brands. How does the combination of design and technology turn light into a recognizable brand signature?
Read moreA few decades ago, securing a car meant a sturdy lock and an alarm. Today, it means defending a rolling, always-connected computing platform – equipped with dozens of Electronic Control Units (ECUs), multiple in-vehicle networks, and high-speed links to the cloud.
Read more